CIA Exam Sample Questions: Part 1, Part 2, and Part 3
Free CIA Exam Sample Questions
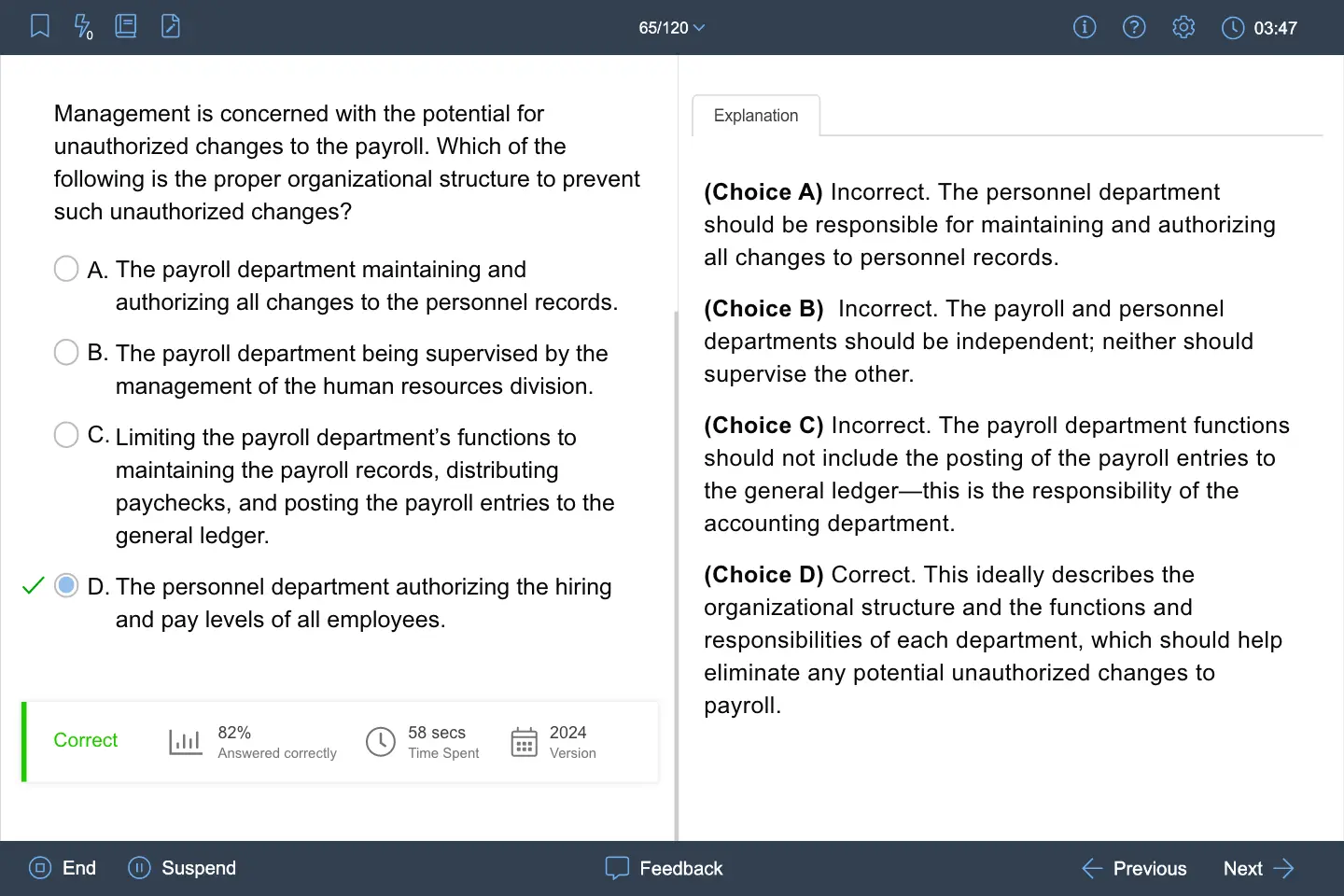
Follow-up activity may be required to ensure that corrective action has taken place for certain findings. The internal audit department’s responsibility to perform follow-up activities as required should be defined in the:
| A. Internal auditing department’s written charter. | ||
| B. Mission statement of the audit committee. | ||
| C. Engagement memo issued prior to each audit assignment. | ||
| D. Purpose statement within applicable audit reports. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Correct. Responsibility for follow-up should be defined in the internal auditing department’s written charter (IIA Standard 1000 – Purpose, Authority, and Responsibility; IIA Standard 2500 – Monitoring Progress).
(Choice B) Incorrect. Follow-up is not specified in the content of the audit committee’s mission statement.
(Choice C) Incorrect. This memo may contain a statement about responsibility for follow-up, but such a statement should be based on the wording and authority of the departmental charter.
(Choice D) Incorrect. Follow-up authority and responsibility may be cited in applicable audit reports, but the definition should be first contained in the departmental charter.
According to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the U.S. Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), what is the proper term for when a chief executive officer (CEO) and chief financial officer (CFO) need to give up their bonuses and incentives based on financial results that later had to be restated or proved to be fraudulent?
| A. Pushback provision | ||
| B. Clawback provision | ||
| C. Pullback provision | ||
| D. Rollback provision |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Incorrect. There is no bad intent with the pushback provision. For example, some governmental policies and laws can be pushed back if citizens protest them.
(Choice B) Correct. The clawback provision requires that the CEO and CFO of a corporation give up bonuses and incentives received based on financial results of their company that later had to be restated or were found to be fraudulent. There is a bad intent on the part of the company management.
(Choice C) Incorrect. There is no bad intent with the pullback provision. For example, retailers can pull back some merchandise from their store shelves if they are deemed to be unsafe.
(Choice D) Incorrect. There is no bad intent with the rollback provision. For example, retailers can roll back their merchandise provision or some laws can be rolled back if citizens protest them.
A tool that generally is not used to manage subjective risk is:
| A. Obtaining more information. | ||
| B. Group discussion. | ||
| C. Systematically identifying and analyzing appropriate methods for dealing with risks. | ||
| D. Severity reduction. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Incorrect. More information is obtained to manage subjective risk.
(Choice B) Incorrect. Group discussion is used to manage subjective risk due to its consensus approach.
(Choice C) Incorrect. If risks have been systematically identified and analyzed, and if decisions have been made regarding the appropriate methods for dealing with those risks, then in most cases subjective risk can be expected to decrease.
(Choice D) Correct. Severity reduction is used to manage objective risk due to its quantitative nature. Because objective and subjective risks are often both present in the same situation, some consideration must also be given to managing subjective risk. In one sense, the techniques applied to objective risk should also affect subjective risk (IIA Standard 2120—Risk Management).
Which of the following is not a contributing factor to a false assurance coming from an internal audit to others?
| A. Measurement gaps | ||
| B. Communication gaps | ||
| C. Expectation gaps | ||
| D. Competency gaps |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Correct. False assurance is a level of confidence or assurance based on perceptions or assumptions rather than facts. False assurance has nothing to do with measurement gaps, which identify problems in measuring something of importance (e.g., production counts, inventory counts, and claims counts).
(Choice B) Incorrect. Communication gaps contribute to false assurances and occur when an internal audit activity’s role, purpose, and scope are not clearly communicated to company management. Communication gaps also result when the required communication is not delivered at the right time.
(Choice C) Incorrect. Expectation gaps contribute to false assurances and occur when company management has an incorrect expectation of the internal audit function related to audit work results.
(Choice D) Incorrect. Competency gaps contribute to false assurances and occur when the auditor’s actual competency level is different from what the auditee’s management requires or expects. Competency gaps are the differences between the expected competencies in terms of knowledge, skills, and abilities (KSAs) and actual KSAs.
According to the COSO report, the internal control framework consists of which of the following?
| A. Processes, people, objectives. | ||
| B. Profits, products, processes. | ||
| C. Costs, revenues, margins. | ||
| D. Return on investment, earnings per share, market share. |
Explanation
(Choice A) Correct. The core of any business is its people—their individual attributes, including integrity, ethical values, and competence and the environment in which they operate. They are the engine that drives the entity and the foundation on which everything else rests. The entity will have its objectives and the processes to achieve those objectives (IIA Standard 2130—Control).
(Choice B) Incorrect. Profits and products are not part of the internal control.
(Choice C) Incorrect. Costs, revenues, and margins are not part of the internal control. Instead, they are part of financial control.
(Choice D) Incorrect. ROI, EPS, and market share are not part of internal control. Instead, they are part of financial and marketing control.
Which of the following uses web-call-center notes and web-chat notes to detect fraud?
| A. Text-based data analytics | ||
| B. Open source data analytics | ||
| C. Visual data analytics | ||
| D. Streaming data analytics |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Correct. Since web-call-center notes and web-chat notes are written in words, text-based data analytics are useful to identify fraud. This analytic is based on matching keywords.
(Choice B) Incorrect. Open source data analytics could use a combination of graphs, tables, figures, and words.
(Choice C) Incorrect. Visual data analytics mainly uses graphs, tables, and figures, not so much words.
(Choice D) Incorrect. Streaming data analytics are performed in real time and in memory where they collect data from electronic sensors to produce time-series data.
An internal auditor in a retail company reports to the corporate director of internal audit. The auditor is assigned to audit a regional division. The audit reports are to be sent both to the corporate office and the division controller in the region. The auditor has been on location for six months and has submitted monthly reports, each month auditing a part of the operation as assigned by corporate internal auditing. This month, for the first time, the auditor has audited the inventory controls, following procedures established by the corporate internal auditing staff.
After seeing the audit report on inventory control, the divisional controller called and requested a meeting with the auditor. At the meeting, the divisional controller loudly and abusively criticized the accuracy of the auditor’s work, the soundness of the auditor’s methods, and the results presented in the reports. In the past, while not always agreeing with the auditor’s conclusions, the divisional controller always had rational discussions and developed appropriate follow-up steps to correct the problems the auditor found.
This particular audit was not the auditor’s best work, and the auditor realizes this. The auditor should:
| A. Defend the work now and try to improve it in the future. | ||
| B. Ask the divisional controller to identify specific areas in which the report is deficient, and, if the objections are justified, revise the report. | ||
| C. Explain the personal problems that kept the auditor from working as hard on this report as could be expected. | ||
| D. Ask for time off for training in the weak areas. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Incorrect. If the auditor really needs to make changes to the report, eventually they will have to be made, and the divisional controller may ask someone else to make them if the auditor refuses to admit any mistakes.
(Choice B) Correct. Asking for specific objections will improve both the auditor’s work and the working relationship with the divisional controller by defusing this situation (IIA Standard 2431—Engagement Disclosure of Nonconformance).
(Choice C) Incorrect. The issue here is work, not personal problems.
(Choice D) Incorrect. Again, the issue here is work and getting it done. The auditor should find out what specific areas need work, revise the report, and apply for related training when it is next available.
The following information is extracted from a draft of an audit report prepared on the completion of an audit of the inventory warehousing procedures for a division.
Findings
[#5]
We performed extensive tests of inventory record keeping and quantities on hand. Based on our tests, we have concluded that the division carries a large quantity of excess inventory, particularly in the area of component parts. We expect this be due to the conservatism of local management that does not want to risk shutting down production if the goods are not on hand. However, as noted earlier in this report, the excess inventory has led to a higher-than-average level of obsolete inventory write-downs at this division. We recommend that production forecasts be established, along with lead times for various products, and used in conjunction with economic order quantity concepts to order and maintain appropriate inventory levels.
[#6]
We observed that receiving reports were not filled out when the receiving department became busy. Instead, the receiving manager would fill out the reports after work and forward them to accounts payable. There is a risk that all items received might not be recorded or that failing to initially record might result in some items being diverted to other places. During our tests, we noted many instances in which accounts payable had to call to receiving to obtain a receiving report. We recommend that receiving reports be prepared.
[#7]
Inventory is messy. We recommend that management communicate the importance of orderly inventory management techniques to warehouse personnel to avoid the problems noted earlier about (1) locating inventory when needed for production and (2) incurring unusually large amounts of inventory write-offs because of obsolescence.
[#8]
We appreciate the cooperation of divisional management. We intend to discuss our findings with them and follow up by communicating your reaction to those recommendations included within this report. Given additional time for analysis, we feel there are substantial opportunities available for significant cost savings and we are proud to be a part of the process.
A major deficiency in paragraph #6 related to the completeness of the audit report is:
| A. The factual evidence for the audit finding is not given. | ||
| B. The cause of the problem is not defined. | ||
| C. The risk is presented in an overdramatic fashion. | ||
| D. The recommendation is incomplete. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Incorrect. The factual evidence comes from observation.
(Choice B) Incorrect. The cause of the problem (or at least the excuse given by the receiving department) is noted. The receiving department does not prepare concurrent receiving reports when it is busy.
(Choice C) Incorrect. This is a well-known risk, and the auditor is not overdramatic in factually detailing the result that might occur if the control deficiency is not adequately addressed.
(Choice D) Correct. The recommendation given is not complete. Receiving reports are being prepared, but they are not being prepared on a timely basis, or concurrently with the receipt of the goods. The recommendation needs to be more detailed (IIA Standard 2410—Criteria for Communicating).
During an audit of a defense contract, the auditor becomes concerned with the possibility of inappropriate charges to overhead. However, when examining the underlying documentation of expenses, the auditor finds that all expenditures are properly supported. All billings show total cost and the application of a percentage overhead rate that appears consistent with previous years. Assume the contract with the defense contractor states that the government will not pay for costs associated with waste or inefficiency on the part of the contractor. Which of the following sources of evidence would be least persuasive regarding potential waste and inefficiency on the part of the contractor?
| A. Management certification that it has not incurred waste or inefficiencies that are not allowed in the contract. | ||
| B. A walk-through of the contractor’s manufacturing and development facilities. | ||
| C. An examination of the nature of expenses incurred to determine their intent and relationship to the contract. | ||
| D. A comparison of contract expense with that of similar projects in the past or similar projects with other companies. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Correct. This is a form of testimonial evidence and is insufficient without significant corroborating evidence. Since management has self-interest in certifying it is free from waste and inefficiency, it is the least persuasive evidence.
(Choice B) Incorrect. A walk-through provides insight on the efficiency of operations and would be an effective first step in establishing the potential need to investigate for waste and inefficiency.
(Choice C) Incorrect. An examination of actual expenditures would indicate whether duplicate expenses have been incurred or whether waste was taking place.
(Choice D) Incorrect. Comparison with similar projects, over time or across projects, would provide insight on possible waste and inefficiency.
The internal auditing department has begun an audit of an automated payroll system. Audit staff members have been trained in the use of an audit software package and have a working knowledge of the database employed for this system but do not have programming experience. In the system being audited, employees report their hours on time sheets, which are keyed each week by an assigned individual in each department.
The transaction file of payroll hours is maintained by the system as a primary source of payroll input. After the department manager reviews the gross hours, the information is released to the online payroll system. The payroll is then processed, and pay stubs are printed and distributed to the employees. All payments are through direct deposit. In order to preserve the confidentiality of the payroll information of employees, detailed reports that reconcile payroll expenses charged to the department are not generated. Management wants to know whether the payroll program is reliable. Given the skill level of the assigned staff, which of the following methods will most likely be applied to test the accuracy of the payroll calculation?
| A. Parallel simulation. | ||
| B. Integrated test facility. | ||
| C. Tagging and tracing. | ||
| D. Mapping and program analysis. |
Explanation
(Choice A) Correct. Use of audit software to perform parallel simulation is an acceptable audit application.
(Choice B) Incorrect. Use of an integrated facility usually requires advance planning before a system is implemented. Installing an integrated test facility after the fact can be quite costly and time consuming.
(Choice C) Incorrect. Tagging and tracing is more difficult to employ than parallel simulation.
(Choice D) Incorrect. Mapping and program analysis requires a strong programming background, which is not available with this audit team.
Which of the following provides encryption as a basic service and becomes a form of double encryption when it is sent through an encrypted tunnel?
| A. Value-added network | ||
| B. Virtual private network | ||
| C. Body area network | ||
| D. Personal area network |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Incorrect. A value-added network is used in electronic data interchange transactions in procurement or purchasing to place purchase orders.
(Choice B) Correct. A virtual private network (VPN) is the application of encryption, data integrity, and authentication protocols to provide a secure connection between a user organization and a remote device or user. When the data stream itself is also encrypted, the use of VPN to send already-encrypted communication through an encrypted tunnel is a type of double encryption.
(Choice C) Incorrect. A body area network is used in medical field when performing an operation on a human body.
(Choice D) Incorrect. A personal area network is used for an individual using personal computers at home, home-office, or in small business.
A company produced and sold 100,000 units of a component with a variable cost of $20 per unit. First quality components have a selling price of $50. The component’s specifications require its weight to be 20 kg. with a tolerance of plus or minus of 1 kg. Unfortunately, 1,200 of the units produced failed the company’s tolerance specifications. These 1,200 units were reworked at a cost of $12 per unit and sold as factory seconds at $45 each. Had the company had a quality assurance program in place such that all units produced conformed to specifications, the increase in the company’s contribution margin from this component would have been
| A. $14,400. | ||
| B. $20,400. | ||
| C. $21,600. | ||
| D. $39,600. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Incorrect. This is equal to $12 × 1,200= $14,400.
(Choice B) Correct. The increase in the company’s contribution margin would be $20,400 and is computed as: [$12+($50−$45)]×1,200.This is equal to $20,400.
(Choice C) Incorrect. This is equal to [$50 – ($20 + $12)] × 1,200= $21,600.
(Choice D) Incorrect. This is equal to ($45 – $12) × 1,200 = $39,600.
Which of the following denial-of-service (DoS) attacks in networks is least common in occurrence?
| A. Service overloading. | ||
| B. Message flooding. | ||
| C. Connection clogging. | ||
| D. Signal grounding. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Incorrect. Service overloading occurs when floods of network requests are made to a server daemon on a single computer. It cannot process regular tasks in a timely manner.
(Choice B) Incorrect. Message flooding occurs when a user slows down the processing of a system on the network, to prevent the system from processing its normal workload, by “flooding” the machine with network messages addressed to it. The system spends most of its time responding to these messages.
(Choice C) Incorrect. Connection clogging occurs when users make connection requests with forged source addresses that specify nonexistent or unreachable hosts that cannot be contacted. Thus, there is no way to trace the connection back; they remain until they time out or reset. The goal is to use up the limit of partially open connections.
(Choice D) Correct. In DoS attacks, some users prevent other legitimate users from using the network. Signal grounding, which is located in wiring closets, can be used to disable a network. This can prevent users from transmitting or receiving messages until the problem is fixed. Signal grounding is the least common in occurrence as compared to the other choices because it requires physical access.
A company that annually reviews its investment opportunities and selects appropriate capital expenditures for the coming year is presented with two projects, called project A and project B. Best estimates indicate that the investment outlay for project A is $30,000 and for project B is $1 million. The projects are considered to be equally risky. Project A is expected to generate cash inflows of $40,000 at the end of each year for two years. Project B is expected to generate cash inflows of $700,000 at the end of the first year and $500,000 at the end of the second year. The company has a cost of capital of 8%.
Net present value (NPV) and internal rate of return (IRR) differ in that:
| A. NPV assumes reinvestment of project cash flows at the cost of capital while IRR assumes reinvestment of project cash flows at the internal rate of return. | ||
| B. NPV and IRR make different accept or reject decisions for independent projects. | ||
| C. IRR can be used to rank mutually exclusive investment projects but NPV cannot. | ||
| D. NPV is expressed as a percentage while IRR is expressed as a dollar amount. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Correct. NPV assumes that cash inflows from the investment project can be reinvested at the cost of capital while IRR assumes that cash flows from each project can be reinvested at the IRR for that particular project. This underlying assumption is considered to be a weakness of the IRR technique.
(Choice B) Incorrect. NPV and IRR make consistent accept/reject decisions for independent projects. When NPV is positive, IRR exceeds the cost of capital and the project is acceptable.
(Choice C) Incorrect. It is the NPV method that can be used to rank mutually exclusive projects while IRR cannot be used for this purpose. The reinvestment rate assumption causes IRR to make faulty project rankings under some circumstances.
(Choice D) Incorrect. IRR is expressed as a percentage while NPV is expressed in dollar terms.
A reader of a statement of cash flows wishes to analyze the major classes of cash receipts and cash payments from operating activities. Which methods of reporting cash flows from operating activities will supply that information?
| A. Both the direct and indirect methods. | ||
| B. Only the direct method. | ||
| C. Only the indirect method. | ||
| D. Neither method. |
Explanation
(Choice A) Incorrect. Only the direct method will supply information about individual classes of gross cash receipts and gross cash payments related to operating activities.
(Choice B) Correct. The direct method reports major classes of gross cash receipts and gross cash payments from operating activities and their arithmetic sum—the net cash flow from operating activities. The indirect method adjusts net income to reconcile it to net cash from operating activities. The indirect method does not report individually the major classes of cash receipts and cash payments from operations.
(Choice C) Incorrect. The direct method, rather than the indirect method, supplies information about individual classes of gross cash receipts and gross cash payments related to operating activities.
(Choice D) Incorrect. The direct method reports major classes of gross cash receipts and gross cash payments from operating activities.
Why Practice with UWorld CIA Review Sample Questions?
Practice from
Anywhere
Questions at or Above
Exam Difficulty
Detailed Performance
Metrics
Breaking Down the CIA Exam
The CIA exam, administered by the Institute of Internal Auditing, evaluates your knowledge of 14 essential auditing domains. Multiple-choice questions on all 3 parts of the CIA exam assess your attention to detail, your reading comprehension skills, and your ability to apply the IIA’s practical and ethical standards to real-world scenarios that commonly impact businesses.
The parts that make up the CIA exam include:
- CIA Part 1: Essentials of Internal Auditing
- CIA Part 2: Practice of Internal Auditing
- CIA Part 3: Business Knowledge for Internal Auditing
To earn a passing score, you must demonstrate strong understanding of areas like the foundations of internal auditing, risk management, and fraud.
How Do CIA Exam Multiple-Choice Questions Work?
When tackling these questions, be sure to read the initial query and all available answer choices carefully. It may surprise you to learn that many CIA instructors describe this exam as a sophisticated reading comprehension test.
The IIA incorporates MCQs questions that:
- Have a single, identifiable and straightforward answer.
- Use tricky phrases like “Select the statement that is not…”
- Include long, multi-paragraph scenarios detailing a specific issue or case.
To succeed on the CIA exam, you must refine your time-management skills while maintaining accuracy when selecting answers.
Challenge and Prepare Yourself for CIA Exam Success
Multiple-Choice Questions That Make a Difference
Your UWorld multiple-choice QBank and mock exam questions use the language, structure, and scenario types most commonly found on Parts 1, 2, and 3 of the CIA exam.

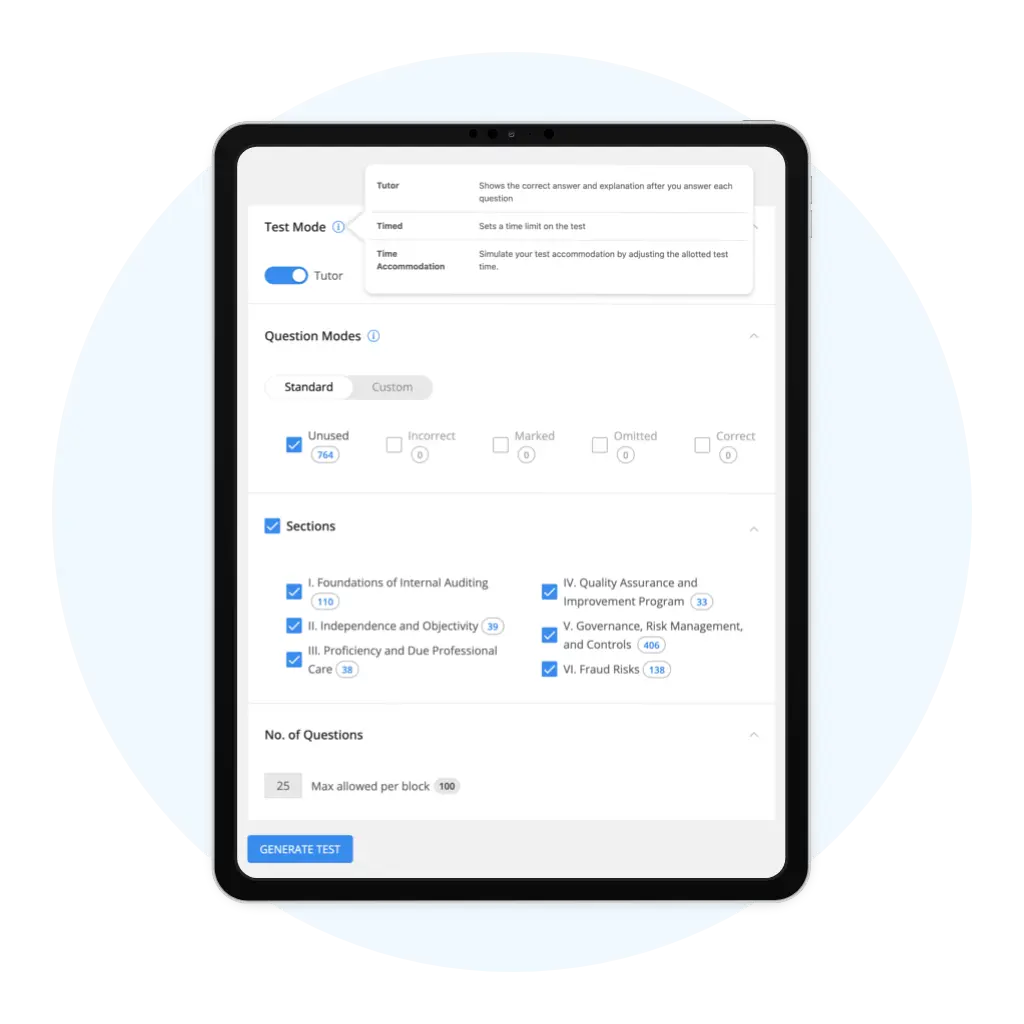
Tutor and Timed Modes for Additional Support
Successful exam preparation requires active learning. When you create a practice exam using your QBank in Tutor Mode, you see all answer explanations after completing each question to make sure you:
- Fully understand what was asked.
- Avoid related mistakes on future questions.
Timed Mode imposes time constraints similar to what you would experience on exam day, enhancing your endurance, your time-management skills, and your ability to apply core CIA exam principles under pressure.
Hear From Our Past Candidates
I only used the QBank, and I am grateful for the huge variety of questions. It's been an amazing feeling getting through two parts of the exam so far, which has encouraged me to get ready for the third.”
I liked having the notes and the Study Guide handy on my computer. The multiple-choice questions were really good in helping me prepare for the exams.”
I chose this course because I read that UWorld provides a more comprehensive option for the CIA exam compared to others in the market. I liked the fact that topics are explained in more detail compared to other courses I have found.”
Frequently Asked Questions
The IIA announced in January 2024 that a new version of the complete CIA Exam Syllabus aligned with the 2024 International Professional Practices Framework (IPPF) will be published in May 2024. The CIA exam will be updated to reflect the new IPPF and revised Global Internal Auditing Standards no earlier than May 2025.