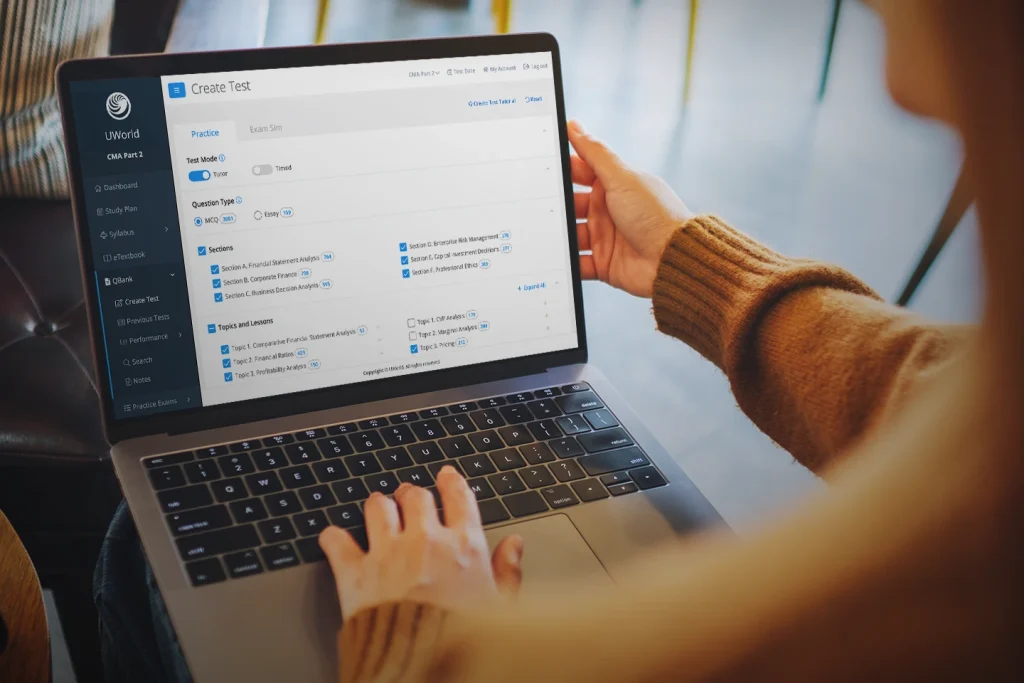
CMA Exam Sample Questions
Part 1 and Part 2
Try It for Free!
Free Sample CMA Exam Questions
Our practice questions are designed to help you understand the why behind each answer choice for every question, and are written by our team of practicing CMAs. Get started below with our strategically-selected multiple-choice samples.
At the end of Year 3, the managers of Guardian Company are planning for Year 4. In Year 3, manufacturing overhead was $349,600, direct labor hours equaled 16,000 hours, and machine hours totaled 48,000 hours. For Year 4, manufacturing overhead is estimated to be $524,400, direct labor hours are estimated at 20,000 hours, and machine hours are estimated at 50,000 hours. If overhead is applied based on direct labor hours, what is the predetermined overhead rate for Year 4 (if necessary, round your answer to two decimal places)?
| A. | $10.49 per direct labor hour. | ||
| B. | $32.78 per direct labor hour. | ||
| C. | $21.85 per direct labor hour. | ||
| D. | $26.22 per direct labor hour. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Incorrect. This amount is Year 4 estimated overhead divided by Year 4 estimated machine hours. Because overhead is applied based on direct labor hours, do not divide by machine hours to calculate the predetermined overhead rate.
(Choice B) Incorrect. This amount is Year 4 estimated overhead divided by Year 3 direct labor hours. When calculating the Year 4 predetermined overhead rate, use estimates from Year 4.
(Choice C) Incorrect. This amount is Year 3 estimated overhead divided by Year 3 direct labor hours. When calculating the Year 4 predetermined overhead rate, use estimates from Year 4.
(Choice D) Correct. The predetermined overhead rate based on direct labor hours for Year 4 equals the estimated overhead for Year 4 divided by the estimated direct labor hours for Year 4. The predetermined overhead rate equals $26.22 per direct labor hour ($524,400 ÷ 20,000 direct labor hours).
Which of the following emerging technologies can help in improving the efficiency of manufacturing plant assembly operations and warehouse operations?
| A. | 3D printing | ||
| B. | Robots | ||
| C. | Virtual reality | ||
| D. | Internet of Things |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Incorrect. 3D printing technology is useful in improving the efficiency and accuracy of product design whether it is a manufacturing product (e.g., an automobile or a vacuum cleaner), clothes, or shoes.
(Choice B) Correct. Robotic technology or robotic process automation (RPA) improves the speed and accuracy of assembling various parts or components in a manufacturing plant, soldering and painting subassemblies and final assemblies of parts, and other labor-intensive tasks. Similarly, robots operate in a warehouse and distribution center to locate the desired product on a warehouse shelf, to place the product in a shipping container, and to get ready for shipping to a customer so the customer order is fulfilled. The overall benefits of RPA include reduced labor costs due to less time to complete tasks, increased speed and accuracy, improved worker productivity (i.e., doing more tasks in less time), reduced human errors from not shipping wrong products to customers, and increased customer satisfaction with faster and more accurate order fulfillment process.
(Choice C) Incorrect. Virtual reality (VR) technology is a leading-edge technology applied to retail business that replicates or simulates the real world through images (goggles) and sounds that can be heard from speakers and headphones (headsets). It creates 3D graphic models to interact with images. A user of the VR equipment is immersed in a real lifelike experience while interacting with computer-simulated environment. VR technology started in video games, pilot training, and motion pictures. The VR technology has entered into medical training, military training, and other kinds of training. The goal of retailers with VR technology is to turn viewers (shoppers) into buyers (customers).
(Choice D) Incorrect. The Internet of Things (IoT) technology is a collection of several diverse and disparate technologies aimed at providing efficiency gains to a business and convenience and comfort to consumers’ day-to-day life at home. Within a business environment, the IoT means connecting or networking several systems and devices and passing data between them to operate as one seamless and cohesive system, providing insights, and requiring management decisions and actions.
All of the following statements concerning currently attainable standards are correct except:
| A. | Currently attainable standards assume machines will be taken off-line for preventative maintenance. | ||
| B. | Currently attainable standards assume employees work at a normal pace. | ||
| C. | Currently attainable standards can only be reached by the most skilled and efficient employees. | ||
| D. | Currently attainable standards are expected to be achieved most of the time. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Incorrect. Currently attainable standards are sometimes called reasonably attainable standards as they can be achieved under normal operating conditions. One example of normal operating conditions is that machines need to be taken off-line for preventative maintenance from time to time to keep them operating properly.
(Choice B) Incorrect. Currently attainable standards are sometimes called reasonably attainable standards as they can be achieved under normal operating conditions. One example of normal operating conditions is that employees work at a normal pace by taking breaks from time to time.
(Choice C) Correct. An organization can use ideal standards or currently attainable standards to develop budgets. Ideal standards can only be reached by the most skilled and efficient employees while currently attainable standards require average workers who are properly trained.
(Choice D) Incorrect. Currently attainable standards are sometimes called reasonably attainable standards as they can be achieved under normal operating conditions. Because they can be achieved under normal operating conditions, they should be achieved most of the time.
Fashionable Purses (FP) is about to begin its annual budgeting process, but would like to make the process more informative. Specifically, FP is facing product demand uncertainty. Management is forecasting that FP will sell around 30,000 purses; however, this amount could be 20% more or 30% less. What tool or method should FP employ this year to make the budget process more informative?
| A. | A zero-based budget | ||
| B. | A flexible budget | ||
| C. | An activity-based budget | ||
| D. | A continuous rolling budget |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Zero-based budgeting demands that all budgeting choices are taken back to a “blank page” to be fully evaluated and, if approved, put into the master budget plan. While this process could be informative to FP management, they will not receive the “what if” information they are seeking in this situation.
(Choice B) Flexible budgets are used to examine possible future (“what if”) scenarios in sales volume. A flexible budget would provide the information that FP management is seeking in this situation.
(Choice C) Activity-based budgeting focuses on identifying and using core activities throughout the organization to establish activity cost rates to assign costs to products, customers, and other business targets based on actual consumption relationships. While this process will be informative to management, it will not provide the (“what if”) information they are seeking in this situation.
(Choice D) Rolling budgets are particularly helpful to organizations that want to avoid an annual master budget planning event that can consume a large block of management time. While it’s true that FP management does plan the budget annually; in this situation, they are not worried about saving time. They are worried about making the budgeting process more informative.
Which of the following statements is correct concerning a company using budgeted output to calculate an allocation rate?
| A. | The company will be more likely to be able to evaluate the cost of unused capacity than if it used practical capacity to calculate its allocation rate. | ||
| B. | The company will be less likely to experience a product pricing death spiral than if it used theoretical capacity to calculate its allocation rate. | ||
| C. | The company will be more likely to have to adjust its allocation rates than if it used practical capacity to calculate its allocation rate. | ||
| D. | The company will allocate less cost to its products than if it used theoretical capacity to calculate its allocation rate. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) This answer is incorrect. Unused capacity can be broken down into unplanned unused capacity and planned unused capacity. Unplanned unused capacity refers to the difference between actual output and budgeted output while planned unused capacity refers to the difference between budgeted output and the denominator used in the allocation rate. By using budgeted output, the company can only calculate the cost of unplanned unused capacity. If it uses practical capacity, it can calculate the cost of planned unused capacity and unplanned unused capacity.
(Choice B) This answer is incorrect. A product pricing death spiral is more likely to occur if budgeted output is used to calculate an allocation rate, since the allocation rate will increase as budgeted output decreases. The higher rate results in a higher selling price, further decreasing budgeted output, which accelerates the spiral. Since theoretical capacity is not likely to change, the allocation rate based on it is also unlikely to change.
(Choice C) This answer is correct. When calculating allocation rates, companies have discretion on what level of output to use for the denominator of the calculation. The choices are practical capacity (output under realistic circumstances), theoretical capacity (output under ideal circumstances), and budgeted output (output expected in the period). One result of using budgeted output is that it increases the likelihood that allocation rates will change from one period to the next. Budgeted output represents expected output for a given period, while practical capacity represents capacity under realistic circumstances. Expected output is more likely to change from one period to the next than is what is “realistic” output. As a result, an allocation rate based on expected output is more likely to change from one period to the next than is a rate based on “realistic” output.
(Choice D) This answer is incorrect. The higher the allocation rate, the more overhead will be allocated to actual output. Since budgeted output can never be higher than theoretical capacity, an allocation rate based on budgeted output can never be lower than an allocation rate based on theoretical capacity.
Take a look at a typical sample question from another provider below. The question shows you what you’ll see on the exam, but that’s not enough to help you pass. Their explanation addresses the right answer choice but does not go the extra mile to explain the wrong choices—so you don’t make the same mistakes on exam day.
Nemo Diving Products, Inc. usually stores its product inventory in a special area within its manufacturing facility. Due to a recent fire, all inventory this month was stored offsite at a cost of $3,000. Some inventory items are normally purchased from Switzerland. This month’s import duty was $2,000. This month’s unreimbursable freight charges on product sold were $4,000. Given the above three costs, what amount(s) are chargeable to inventory vs. chargeable to expense?
| Inventory | Expense | |||
| A. | $2,000 | $7,000 | ||
| B. | $9,000 | $0 | ||
| C. | $5,000 | $4,000 | ||
| D. | $3,000 | $6,000 |
Explanation:
“A” is correct.
Import duty should be charged to inventory. The other two items are expensed as incurred. The $3,000 warehousing cost is not chargeable to inventory since it is not a “usual” cost. To be included in inventory, a cost must be usual, necessary and make the item ready for sale. The $4,000 freight charge is a selling expense.
“B” “C,” and “D” are incorrect per the above explanation.
The management team at an organization has recently begun to bond certain employees to prevent cash embezzling and other unethical activity. Is this an appropriate step?
| A. | No, bonding employees has not been proven to prevent unethical activities linked to cash activities, back reconciliation, or depositing cash receipts. | ||
| B. | Yes, bonding employees helps protect the organization from potentially unethical activity, including but not limited to embezzling cash, misreporting cash amounts, or other fraudulent actions. | ||
| C. | Yes, instituting an employee bonding program protects employees from top-down pressure initiated by management to boost financial performance. | ||
| D. | No, employee bonding is only linked to the technology processes underlying financial reporting, so it would not have any benefit for the firm. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Incorrect. Bonding employees, especially at larger organizations that have standalone treasury and/or accounts receivable functions, is a logical step to help offset the risk of unethical activity.
(Choice B) Correct. Bonding employees is a logical step that protects the organization from potentially unethical activities by employees, especially concerning cash-related activities. It does not stop the employees from committing such actions, but provides funds to mitigate the impact.
(Choice C) Incorrect. Employee bonding protects the organization from unethical actions of employees, and not employees from top-down pressure from management.
(Choice D) Incorrect. Bonding employees is directly linked to cash-related activities, and protecting the firm from unethical activities connected to cash-linked actions.
Which of the following is an example of the loss event data technique of identifying events within an Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) approach to risk management?
| A. | The head of HR holds a meeting with employees to get their ideas on possible steps to improve the hiring process. | ||
| B. | A company maps out the process for conducting position searches and hiring new employees. | ||
| C. | A company considering outsourcing its payroll function consults a list of events related to outsourcing payroll developed by a consulting firm. | ||
| D. | A delivery company analyzes losses from accidents its vehicles were in to see if any patterns emerge. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) This is an example of the facilitated workshop and interviews technique since this technique involves drawing on the accumulated experience of all involved parties through structured discussions and interviews. Therefore, this is an incorrect answer.
(Choice B) A company mapping out the process for conducting position searches and hiring new employees is practicing the process flow analysis technique since this technique involves assessing the steps an organization goes through in order to identify events of interest. Therefore, this is an incorrect answer.
(Choice C) This company is practicing the event inventories technique since this technique involves using lists of generic events related to a particular project as a starting point for event identification. Therefore, this is an incorrect answer.
(Choice D) This is an example of the loss event data technique since this technique involves analyzing past data on loss events to assess trends. Therefore, this is the correct answer.
Which of the following statements about contribution margin is true?
| A. | A decrease in variable administrative expenses per unit will decrease contribution margin per unit. | ||
| B. | A decrease in fixed administrative expenses per unit will not impact contribution margin per unit. | ||
| C. | An increase in variable administrative expenses per unit will increase contribution margin per unit. | ||
| D. | A decrease in variable administrative expenses per unit will not impact contribution margin per unit. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Incorrect. This statement is not true. A decrease in variable administrative expenses per unit will increase, not decrease, contribution margin per unit as a smaller variable cost per unit will be subtracted from the sales price when calculating contribution margin per unit.
(Choice B) Correct. This statement is true. Contribution margin represents the amount of revenue left over after all variable costs have been paid. Contribution margin per unit is the selling price less variable costs per unit. Changes in variable costs per unit impact the contribution margin per unit while changes in fixed costs per unit do not. Since the choice involves a change in fixed administrative expenses, there will be no impact on the contribution margin per unit.
(Choice C) Incorrect. This statement is not true. An increase in variable administrative expenses per unit will decrease, not increase, contribution margin per unit as a higher variable cost per unit will be subtracted from the sales price when calculating contribution margin per unit.
(Choice D) Incorrect. This statement is not true. A decrease in variable administrative expenses per unit will increase contribution margin per unit as a smaller variable cost per unit will be subtracted from the sales price when calculating contribution margin per unit.
Which of the following statements concerning earnings volatility resulting from foreign currency fluctuations is not correct?
| A. | Investors and management are not likely to be concerned about earnings volatility resulting from foreign currency fluctuations as an international business provides diversification to a company’s earnings and cash flow. | ||
| B. | Investors and management are more likely to be concerned about volatility arising from foreign currency transactions than from volatility arising from foreign currency statement translation. | ||
| C. | Management can take steps to reduce exposure to foreign currency fluctuations arising from transactions through hedging. | ||
| D. | Management can take steps to reduce exposure to currency fluctuations arising from the translation of foreign currency statements by matching assets and liabilities denominated in a foreign currency. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) Correct. While an international business can provide diversification to a company’s earnings and cash flow, the volatility resulting from foreign currency fluctuations can have a negative impact on a company. While it can be reduced through hedging and other means, it still is something investors and management are likely to be concerned about.
(Choice B) This answer is incorrect. When foreign currency fluctuates in value, the cash flows associated with foreign currency transactions (such as sales made in a foreign currency) also fluctuate. However, foreign currency fluctuations do not result in changes in cash flow when financial statements are translated. Therefore, investors and managers are more likely to be concerned about volatility arising from foreign currency transactions than from volatility arising from foreign currency statement translation.
(Choice C) This answer is incorrect. Hedging can reduce exposure to foreign currency fluctuations.
(Choice D) This answer is incorrect. Matching assets and liabilities denominated in a foreign currency (sometimes called a balance sheet hedge) can reduce exposure to foreign currency fluctuations arising from foreign currency statement translation.
Which of the following is not a reason pricing decisions might differ at various stages of a product’s life cycle?
| A. | There are different levels of production efficiency at various stages of a product’s life cycle. | ||
| B. | A company’s customers have different after-purchase costs at various stages of a product’s life cycle. | ||
| C. | There are different levels of competition at various stages of a product’s life cycle. | ||
| D. | A company has different goals for a product at various stages of a product’s life cycle. |
Explanation:
(Choice A) This answer is incorrect. Production efficiency tends to be the highest during the maturity stage of the product life cycle and lowest during the introduction stage. As production efficiency increases, manufacturing cost per unit decreases. The difference in manufacturing cost per unit results in different pricing decisions.
(Choice B) Correct. There are four stages in the product life cycle: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Capacity usage, investments, and competition are likely to be different in the various stages. As a result of these differences, pricing decisions are likely to be different in the various stages. However, after-purchase costs for customers are associated with whole-life costing, not a product’s life cycle.
(Choice C) This answer is incorrect. Competition levels differ across the product life cycle. When competition is relatively high, demand is price elastic. When competition is relatively low, demand is price inelastic. The difference in price elasticity results in different pricing decisions.
(Choice D) This answer is incorrect. Companies have different goals at different stage of the product life cycle. For example, a company is looking to build market share in the introduction stage and to differentiate its product from competitors in the maturity stage. The difference in goals results in different pricing decisions.
Take a look at a typical sample question from another provider below. The question shows you what you’ll see on the exam, but that’s not enough to help you pass. Their limited explanation addresses the right answer choice but do not go the extra mile to explain the wrong choices—so you don’t make the same mistakes on exam day.
Which of the following is an item with high earnings persistence?
| A. | Extraordinary gain | ||
| B. | Extraordinary loss | ||
| C. | Gain on disposal of old equipment | ||
| D. | Sales from a new product |
Explanation:
D is correct.
Additional revenue from a successful new product and lower costs attributable to improved operating efficiency are examples of high persistence items. Items of low persistence include extraordinary items or one-time or rare transactions such as gains and losses on disposals of capital assets. Zero-persistence items also exist, for example the immediate expensing of intangibles.
Get questions straight to your inbox for CMA Parts 1 and 2 each week.
Why Practice with UWorld CMA Review Sample Questions?
Mirror the Prometric
Interface
Questions at or Above
Exam Difficulty
8 out of 10 Pass
with Us
Breaking Down the CMA Exam
The CMA exam evaluates your knowledge of 12 essential management accounting competencies, your attention to detail, and your ability to apply IMA’s ethical standards to real-world scenarios that commonly impact businesses.
Learn everything you need to know about the CMA exam.
How Do the Question Types Work?
Multiple-Choice (75% of Your Score): When tackling these questions, be sure to read the initial query and all available answer choices carefully. The ICMA incorporates MCQs questions that:
- Have a single, identifiable and straightforward answer.
- Include multiple values in a single answer option formatted in columns.
- Use tricky phrases like “Select the statement that is not…”
- Offer multiple correct answers, but you must select the best one(s).
Essays (25% of Your Score): Management accounting professionals must demonstrate strong written communication skills. The essay section evaluates your ability to:
- Assess a business situation.
- Offer the best solution or path forward based on core CMA exam principles.
The essay section comes after you have answered at least 50% of your multiple-choice questions correctly, so you must build up mental endurance to effectively tackle the writing portion.
Want More Free CMA Questions?
CMA Exam Question Format
Multiple-Choice Questions That Make a Difference
Our multiple-choice QBank and mock exam questions use the language, structure, and scenario types most commonly found on Parts 1 and 2 of the CMA exam. We also incorporate retired ICMA questions, so you know you are practicing with material reflecting what you will experience on exam day.
A tip for effective studying—reviewing all answer explanations will help you avoid related mistakes on future questions.
Essay Questions Designed to Challenge You
Formerly Wiley CMA, UWorld’s 70+ CMA exam essay questions help you boost your time-management skills, apply the concepts you’ve learned from your lectures and study guide, and start thinking like a practicing CMA. As you would on the exam, your goal is to use core CMA competencies to solve common business scenarios.
Another study tip—as you approach exam day, do your practice essays after spending at least an hour answering multiple-choice questions to replicate real testing conditions. The key is to increase your mental stamina while maintaining accuracy.
Hear From Our Past Candidates
The Online Test Bank gives you the required confidence before appearing for the exams! I referred to UWorld (formerly Wiley CMA) for my CMA exam prep and cleared both the parts in the 1st attempt."
Video lessons and the textbook contents are bite-sized and can be learned quickly. Even if you have about an hour to spare, you can complete one sub-topic [...] This is a huge plus in my perspective.
UWorld CMA Review (formerly Wiley CMA Review) prepares you not only for the questions, but for the whole exam experience so you don’t have any surprises during the real CMA exam.”
Frequently Asked
Questions
There are two types of questions on the Part 1 and Part 2 CMA exams—multiple-choice and essays.
Both Part 1 and Part 2 feature 100 multiple-choice questions and 2 essay scenarios each. Multiple-choice questions are worth 75% of your score, while the essay portion is worth the remaining 25%.
The IMA states that exam difficulty varies from test form to test form, regardless of exam window. This means some test forms may have more challenging questions than others. To make sure all candidates are graded fairly, the ICMA uses statistical equating methods so all passing scores are generated fairly.
The best way to prepare yourself for a challenging test form is to practice with questions at or a higher difficulty level than what you would encounter on the actual exam.