The filing of an involuntary bankruptcy petition under the Federal Bankruptcy Code
Below is the code for an example image modal link
Flashcards
/* -- Un-comment the code below to show all parts of question -- */
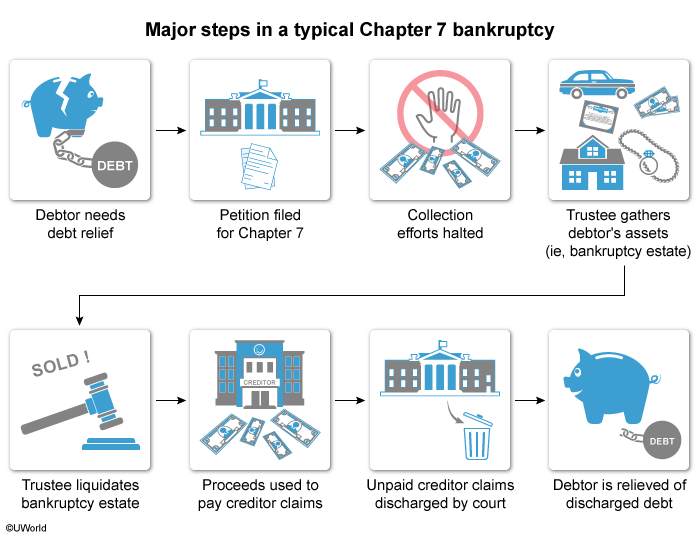
An involuntary bankruptcy occurs when unsecured creditors file a petition to place a debtorA person or entity that borrows money from a lender (ie, creditor) and agrees to repay the amount borrowed, plus interest. in bankruptcy. The petition can be filed under either the liquidation provisions of Chapter 7A form of bankruptcy whereby the debtor's assets are turned over to a bankruptcy trustee, who sells them and uses the proceeds to try and satisfy creditor claims. Any unsatisfied claims are then discharged by the bankruptcy court."> or the reorganization provisions of Chapter 11A form of bankruptcy where the debtor continues to operate its business while it formulates a plan with the creditors to repay a portion of the debt and discharge the remainder. This type of bankruptcy is typically used by corporations and partnerships.. Filing the bankruptcy petition stops all creditorA person or entity that lends money to a borrower (ie, debtor) in return for repayment of the amount of the loan, plus interest. collection efforts, including the enforcement of judgment liensA legal interest in property used to secure payment of a debt or performance of an obligation. against property in the bankruptcy estate.
Filing an involuntary petition is most important in a Chapter 7 bankruptcy, in which all the debtor's secured and unsecured nonexempt propertyAny property of a bankruptcy petitioner that is not statutorily exempt from control by the bankruptcy trustee. This includes any bank accounts and the value of real and personal property beyond the exemption limits. is placed in the bankruptcy estate for liquidationWhere the debtor's assets are turned over to a bankruptcy trustee, who sells them and uses the proceeds to satisfy creditor claims. Any unsatisfied claims are then discharged by the bankruptcy court. Usually done in a Chapter 7 bankruptcy.. The liquidation proceeds are used to satisfy creditor claims. If the judgment lien holder's collection efforts were not stopped, the lien holder could seize the property, removing it from the bankruptcy estate. This would mean fewer assets to liquidate and fewer proceeds to distribute among the other creditors.
(Choice A) Exempt propertyProperty (eg, reasonable alimony, social security benefits) of a bankruptcy petitioner that is statutorily exempt from control by the bankruptcy trustee. is not part of the bankruptcy estate. However, liens on exempt property can be discharged (terminated).
(Choice B) Filing the petition does not terminate all security interests An enforceable legal right that allows a creditor to seize a debtor's collateral and sell it if the debtor defaults on a loan. in the property in the bankruptcy estate; however, they will eventually be terminated when the assets are sold in the liquidation.
(Choice C) Debtors can still incur new debt while in bankruptcy. This often occurs in Chapter 11 bankruptcies, in which the debtor still operates a business during the bankruptcy and needs to incur debt for ongoing operations.
Things to remember:
Filing a bankruptcy petition stops all creditor collections efforts, including the enforcement of judgment liens against property in the bankruptcy estate.